The Michigan (Matching) MODEL OF HRM, Meaning, Diagram, Advantages: This model of hrm is also known as the “Fit model“; or must approach to human resource management. Essentially, this requires close alignment of HR strategy with overall corporate strategy. Therefore, it limits the role of HR to a responsive organizational function and does not emphasize the importance of social and other external factors.
Also See Our New Site: Okay Calculator
Also See: Fombrun Model of HRM
For example, it’s hard to see how current concerns about work-life balance fit into this model. Here in this post we will learn everything about MICHIGAN (Matching) MODEL OF HRM with diagram, advantages, disadvantages and working process.
Also See: HRM Models
MICHIGAN (Matching) MODEL OF HRM
Michigan Model of Hrm has Originated From the Writings of
Michigan or Matching model of hrm has orginated from the writings of C. Fombrun, Noel Tichy and M. Devanna who discusssed it in charectiristic manner in thier book named strategic human resource management in 1984 and hence The Michigan Model was developed in 1984 by the Michigan Business School in the United States. The Michigan (matching) model explains strategic human resource management, which focuses on leadership, business groups, and the new workforce. The main motive of the model was to adapt the formal structure of the organization, its new strategies and policies to the human resources system.
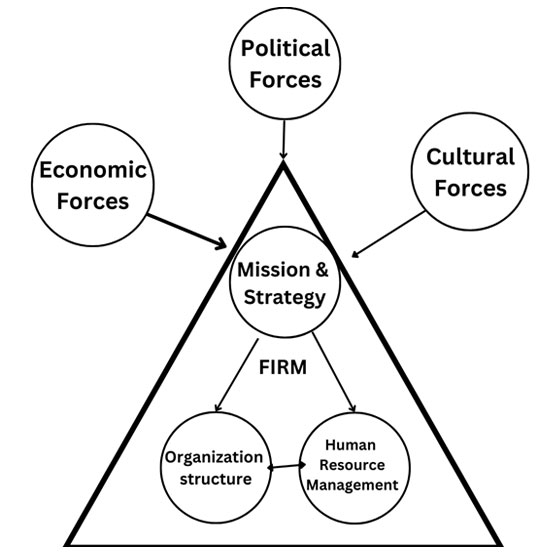
This helps to better implement the strategic goals of the organization. They viewed the company’s people as strategic assets that represent a competitive advantage. Its components include selection, scoring, development, and rewards. The model combines compensation, evaluation, development and selection, which means that there must be a horizontal alignment. Emphasizes market performance and organizational development.
Also See: Human Resource Development
WORKING OF MICHIGAN (matching) MODEL
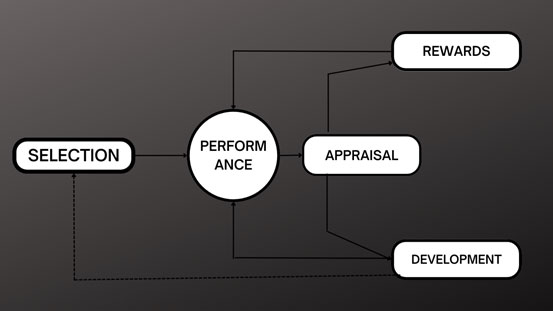
The Michigan Model shows that there is an HR cycle in people management that affects individual and organizational performance. The four functions of this cycle are described as follows:
- Selection: Suitability of available human resources for the positions
- Performance: Evaluation and management.
- Rewards: Focus on organizational performance. The reward system is one of the most underused and poorly managed management tools to increase business performance.
- Development: Development of a quality employee.
Also See: Dave Ulrich HR Model
Efficiency is a function of all HR components: selecting the person best able to carry out the tasks defined by the structure, evaluating their performance in order to ensure a fair distribution of enabling rewards, linking employee motivation through rewards to high performance, and developing employees to improve their current job performance as well as prepare them for roles they may fill in the future.
The Michigan Model is a “hard” HRM because it relies on strategic control, organizational structure, and people management systems. It recognizes the critical importance of motivating and rewarding people, but primarily focuses on leading people to achieve strategic goals. A company with strict human resources management would have a management style that treats employees self-servingly, primarily as a means of achieving the company’s goals. His leadership would strive to run the organization rationally and achieve a “fit” between the strategy, structure and human resources systems of the organization.
Also See: Harvard Model of HRM
ADVANTAGES OF MICHIGAN (matching) MODEL
- Cost effective: No emphasis on employee development or training. Employee management and monitoring costs are minimal.
- Faster Decision Making: Includes one-way communication. Therefore, the decision-making takes place at the management level. Employees have no decision-making authority.
Also See: Standard Causal Model Of HRM: Definition, Features, Process
DISADVANTAGES OF THE MICHIGAN MODEL
- Employee Demotivation: Employees are undervalued, their skills, abilities and development are not considered.
- High absenteeism and turnover: Dissatisfaction among employees leads to high turnover.
- Ineffective Recruitment Practices: Recruitment depends on an employee’s ability to do the job.
- This model ignores stakeholder interests and situational factors.
- The model is context sensitive to political, economic, and cultural forces.
Also See: Guest Model of HRM
CONCLUSION
The Michigan model could be characterized as “hard” HRM because it emphasizes treating employees as a means of implementing corporate strategy, a resource that is in used in a calculation and is purely rational. Hard HRM focuses more than soft HRM on using people as assets and as a means to the organization’s competitive success.
Also See: ASTD Model Of HRM
If you liked this MICHIGAN MODEL OF HRM then please share this with your friends
Also See: Storey Model Of Hrm: Definition and Components
The presentation was good but atleast give more strength and weakness of the model and how the model is really applicable on today setting
Thanks for the comment…we will add more info regarding this topics.