Do you know what exactly the Harvard Model of human resource management is? What does it actually entail? If not, then you are at the right place as here we are going to discuss all ins and outs of this model below. Let us begin to get into the depth of this model.
Also See: Dave Ulrich HR Model
An outline of Harvard Model of HRM
Simply put, the Harvard framework of Human Resource is a HR-based model that is more like a holistics approach to human resource and comprising various levels of outcome. The most vital assignment in a firm is the Human Resource that includes all divisions of staff. An organization is quite prone to achieve all motives if the representatives are utilized successfully. In the same way, how best you can arrange staff in a business firm can be highly helpful to accomplish all goals with a perfect human resource utilization. Vital ramifications are there in the management of human resources and it indicates to looking out for some better methods that would be profitable to the organization.
Also See: HRM Models- Definition, Types with Advantages and Disadvantages
Harvard Model of HRM: Complete Detail with Diagram
The Harvard model of Human resource is the vital model of human resource. It is all based on the Paauwe & Richardson work of 1997 and established a nuance on the above-mentioned model with regard to that of HR operations.
Harvard Model: A story behind it
In 1984, The Harvard Model was developed by Beer et al for human resources. He believes that many of the pressures have passed by HR these days and the pressure needs to be eliminated. It can be done by keeping long-term perspectives such as control over people as well as potential assets instead of the variable cost only. As a result of that, Beer approached the human resource management model of Harvard. The motive of the model is to sort out all pressures that may happen in the HR department of the business firm. All these pressures may comprise the management decisions that affect all organization and workers relationships in addition to all policies of the management.
The Harvard approach defines a mutuality element in all sorts of businesses that is a concept that is parallel to the people management system of Japan as it is observed in the early period. Employees are the vital stakeholders of a business firm. All of them have their own needs as well as concerns with other groups likewise customers and shareholders.
Also See: Guest Model of HRM with Diagram
Four different areas of Harvard Models
The Harvard Model of HR outlines the four different areas of HR that we have mentioned below:
- HR Flows: The flow of human resources consists of placement, recruitment, appraisal, selection, termination, promotion and so on.
- Reward systems: There should be motivation along with a pay system that can help in encouragement of the employees.
- Employee Influence: There ought to be a delegated level of responsibility, power as well as authority.
- Work Systems: It is the definition of work as well as people alignment.
It leads to Four C’s or HR policies that have to be accomplished are Commitment, Competence, Congruence, and Effectiveness of the cost.
Also See: MICHIGAN MODEL OF HRM
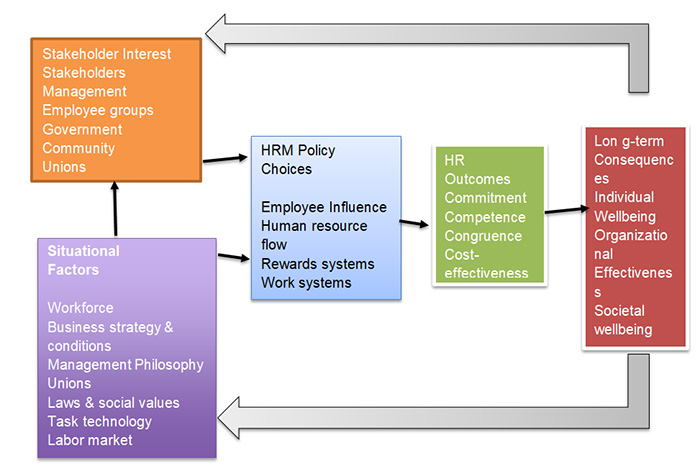
Diagrammatic presentation of Harvard Framework
The Harvard Map of Human Resource Management is a model of all strategies of human resources that comprises six different components that are mentioned as below.
Get more into the Harvard model of HRM: Vital Considerations
Beer, developer of this model, argued when the organization’s general managers determine some policies and practices of human resources for their organization but there was a need for some methods to calculate the appropriateness of all such policies. Beer devised a famous model, called Harvard Map, of Human Resource Management.
Also See: Approaches to HRM: & Different Kinds Of Approaches
This Harvard map relies on an analytical approach & offers a broad impression of all consequences as well as determinants of Human Resource Policies. It indicates the policies of HR that are highly influenced by two vital considerations as given below:
- Situational factors
In the business environment or inside the firm likewise law & societal values, the conditions of labor market, workforce, union, business strategies, and the management of the philosophy. As per Beer, all such factors restrict the formation of all HR policies, but it may get influenced by the policies of human resources.
In the similar manner, there are some situational factors that have an influence on the interests. These situational factors include the characteristics of the workforce, unions and all other factors as included in the 8-box model. The 8-box model was developed by Paul Boselie and includes all external as well as internal factors that affect the operations of HR.
Also See: Contextual And European Model Of HRM
- Stakeholder interest
The model begins with the interest of the stakeholders from the left side. These stakeholder’s interests define all policies of human resources. It includes all management employees, community, shareholders, and government. Beer et al also argued that all policies of Human resources ought to get influenced by the stakeholders. If not, in any case, then the organization will not be able to fulfill the needs of the stakeholders in the long term & also, tagged as a failure of the business firm.
- Strategic HRM
When it is done in a good manner, then the policies of HRM lead to the outcomes of Human Resource Management. It comprises cost-effectiveness, competence, retention, and commitment. It can also be defined as a way to decide on the plans as well as intentions of a business firm seeking out the relations between the process & procedures of the human resources such as recruitment, selection, benefit, training, etc. and employment.
- Long-term Consequences
All these positive outcomes of HRM result in some long-term consequences. It can be organizational, societal and individual.
Also See: Importance of Motivation in HRM?
Factors affecting HRM policies
It has also contended that all policies of human resources might have both sudden outcomes and long-term consequences. Also, managers can affect various factors through its policies that they make, involving:
- The overall employee’s competency
- Employee’s commitment
- The Congruence degree among employees’ goals & that of the business firm
- The whole cost-effectiveness of all practices of Human resources
Beer Et Al has also mentioned that the above-mentioned four Cs don’t indicate all criteria that the policy makers of human resource might use to assess and evaluate HRM effectiveness but consider it as a reasonably thorough even though they advise that the readers may add on some extra factors varying by circumstances.
The bottom line
At the very end, the Harvard model of HRM proffered by Beer is practiced by resolving all problems of historic personal management of employees. Even though stakeholder theory is a central part of the Harvard model, it has a broader scope than Human Resource Management and developed outside the boundaries of Human resource literature.
Also See: Trade Union in HRM, Objectives, Types, Functions and Role
It is a situation where the organization’s definition in terms of motives, activity lists, policies & strategies, and breaking down the roles of the HR department and only in case if it matches with the organization’s circumstances.




I love Beer Et Al analysis of the strategic human resource management model.
But would wish to pursue more of the HRM studies at an advanced level. Any PhD scholarship study opportunity